The pandemic has created opportunities for plenty of remote solutions and software. Technologies used for video conferences or virtual meetings have replaced face-to-face interactions.
Virtual Desktop Infrastructure is also known as desktop virtualization or thin-client computing has been in demand for IT and telecom organizations. In an environment where work from home is a necessity, VDI promotes the trend of BYOD (Bring Your Own Device).
Before we understand “how VDI works” as well as its “pros and cons of implementing and using a VDI”, it is important to address “What is Virtual Desktop Infrastructure?”
What is Virtual Desktop Infrastructure?
What is Virtual Desktop Infrastructure?
Virtual Desktop Infrastructure is the technology that hosts desktop operating systems. The systems are hosted on a central server.
It creates and manages desktop environments and applications. Users can easily access the applications and services remotely from their devices.
Virtualization solutions run VDI deployments and create Virtual Compute Systems. The systems are also known as Virtual Machines (VMs).
VMs help organizations process various applications and operating systems. The processing runs on a single host server in the data center.
The Types of Virtual Desktop Infrastructure and what is the Difference?
- What is a Persistent Virtual Desktop Infrastructure?
It is a VDI technology that connects a user to the same desktop. It enables users to customize the desktop as per their requirements.
The changes and customizations are saved even after the user reconnects. This is what distinguishes a Persistent Virtual Desktop Infrastructure, where the environment is set according to a user’s needs.
- What is a Non-Persistent Virtual Desktop Infrastructure?
Non-Persistent Virtual Desktop Infrastructure is what allows users to connect with universal desktops. Here, no changes made on the desktop are saved.
As there is no need to conserve personalized desktops it is easier and cost-effective to manage. Organizations that run a limited set of tasks or do not require personalized desktops for users often depend on Non-Persistent VDI.
How does VDI Work?
The question “What is Virtual Desktop Infrastructure?” is addressed, “How it works?” is an important query.
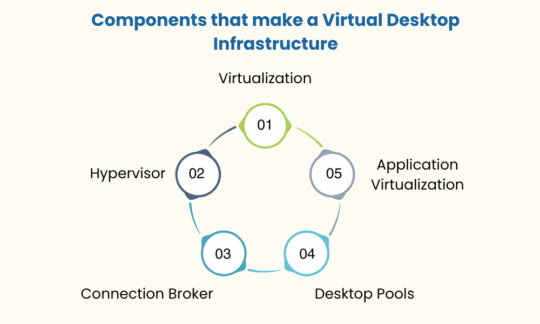
The Components that make a Virtual Desktop Infrastructure Work
-
- Virtualization: It is the solution that separates the system architecture into various layers. It helps in case of a hardware failure where a virtual solution is required to temporarily replace the physical solution.
- Hypervisor: It is the software that separates an Operating System from the hardware. It helps create virtualized infrastructures and breaks down the hardware into many VMs.
- Connection Broker: It is a program that connects a user to the desktop actions. It undertakes the task of authenticating users and assigning them to their respective desktops.
- Desktop Pools: It is a set of desktops that are configured based on their functions. It is created to represent different departments and their functions in an organization.
- Application Virtualization: It is the technology that generates a virtualized application image. The image is replicated to all virtual desktops in the desktop pool for the simple and hassle-free deployment of applications.
How does it work?
-
- A user logs into the desktop using their access. The user is then authenticated by the connection broker.
- Once the authentication is successful, the connection broker assesses the request. It then allows the user to access their desktop in the desktop pool.
- Then, the hypervisor generated many VMs for the Host Virtual Desktop. The hypervisors are installed in the server, which allows them to combine and migrate resources from different desktops and servers.
- The admin can monitor and control the virtual desktop. It switches off the desktops in case the user is not active, which gives way to accommodate more users.
- The desktop image is then mirrored from a master desktop. The master desktop is then linked to all other desktops also known as cloning.
- There are two types of cloning:
- Linked Cloning: The virtual disk of the master desktop is connected to all other desktops. This allows the data of users to be saved separately, saves space on the server, and keeps all the cloned desktops linked to the master desktop.
- Full Cloning: The cloned desktops are independent of the master desktop and their functions are not linked. Here, all the desktops use separate disk spaces for their data.
- A Virtual Desktop Infrastructure management software is used to generate desktop pools. The admin manages the desktop pools, allocates new desktops, creates new pools, and builds policies.
What are the Main Features of a Virtual Desktop Infrastructure and How is it useful for Businesses?
-
- VDI delivers desktops using VMs. The desktops are either hosted on-premise or in the cloud.
- The virtual desktops run in the VMs on a central server within the infrastructure. The VMs are host-based. It allows numerous actions to run that are used by the single server in the data center.
- VDI deployments are developed on a single-tenant model. It offers organizations complete control over the configuration and distribution of resources.
- Organizations are in complete control of the installation, maintenance, and management of VDI deployments.
- VDI works as an alternate form of virtual desktop delivery.
- VDI solutions for businesses provide virtualization for multiple users.
- Cloud-based VDI solutions are known as Desktop As A Service (DaaS). It offers an easy and faster technique to configure a VDI.
What are the Pros and Cons of Virtual Desktop Infrastructure and How is it Affecting Organizations?
Virtual Desktop Infrastructure is what improves user mobility and remote access. It authenticates users from approved and compatible endpoints at any location.
Here are the pros and cons of implementing Virtual Desktop Infrastructure and how is using it affecting businesses:
Pros of a VDI
Here is a list of the pros of a Virtual Desktop Infrastructure and What is reserved for Organizations:
-
Accessibility:
Setting up a VDI provides user accessibility for employees. It only conveys simple input and output data.
It enables organizations to purchase devices that are only compatible with official use. It allows employees to access the data and applications from different locations.
-
Security:
VDI assures high security and protection of organization data. It limits the transfer of data from devices reducing the number of attacks.
Sensitive data is stored on the VDI server. It leads to a reduction in the use of hardware and data transfer through network connections.
-
Performance:
VDI servers aim to attain a faster and enhanced quality of performance. It supports applications and eliminates the run-time on user devices making space for more functions.
It also helps improve the conditions and vitality of the devices. It reduces system lags by regularly testing and tuning the performance of the VDI.
-
Hardware Requirement:
The central operating system in VDI makes sharing and transferring data easy. It reduces the usage of hardware to store, share and maintain the data.
VDI promotes the culture of “BYOD” or ``Bring Your Own Device” programs. It in turn saves time and effort for IT and easily streamlines users and their devices.
-
Centralization:
One of VDI’s biggest benefits is its ability to run an OS and other major functions centrally. It enables the data to remain on the server and is only accessible by authentic users and devices.
The VDI environment is completely controlled, managed, and maintained by a data center. It also increases security benefits and the minimum the potential threat of data loss.
-
Flexibility:
VDI offers organizations device flexibility. It allows users to authenticate, access, and use virtual desktops without installing additional hardware.
It offers flexibility to end-users and their devices. It means that a user can access a virtual desktop by using multiple devices that are authorized.
Cons of a VDI
Here are the cons of a Virtual Desktop Infrastructure and What is required by Organizations:
-
Additional Support:
VDI demands constant and dedicated support from the IT department. Small and Medium Enterprises may opt for a DaaS solution.
DaaS would save efforts on installing a physical server. DaaS will also eliminate the requirement of a dedicated IT team that manages the server, devices, applications, etc.
-
Cost:
Organizations may have to invest a heavy amount in VDI hardware. It may also incur additional costs to virtualize the applications.
However, VDI also saves cost by reducing outages and downtime leading to more productivity. VDI Access could occur using inexpensive thin clients and utilize resources from remote servers.
Conclusion:
The article answers questions like, “What is Virtual Desktop Infrastructure?”, “How it Works?”, and “What are the pros and cons of implementing VDI?”.
According to sources, “The benefits of desktop virtualization are tempting to almost any company and end-user:
-
- Access documents and applications from anywhere, on any device
- Increased data security
- Easier desktop provisioning and troubleshooting
- Making BYOD simple and attainable”
Experts predict that the global market for VDI could reach $19.8 billion by 2031 with a CAGR of 8.3%.
Also Read:
List of 10 Help Desk Management Best Practices: You Should Be Aware Of
Application Virtualization in Cloud Computing: Working, Role & Tools