Losing access to data can bring adverse effects to the organizations.
With cyberattacks on the rise, it becomes essential for the organization to protect its data and be prepared with recovery plans to be online quickly and continue with business operations.
The hot site and cold site are two recovery plans that an organization can look up to in case of any disaster strike.
A hot site can be defined as the backup site that stores the data in real-time and is quickly operable in any disaster strike.
Whereas, in a cold site, the customer provides the hardware and other facilities like office space and other technical requirements for the data storage.
Exploring the Difference Between Hot Site vs Cold Site
A mirror image of the existing data center website is created within a hot site, and entire data is stored in real-time with specialized software.
A hot site allows the organization to return to its working environment within the quickest possible time.
A hot site is a ready-to-go website and is more popular among organizations that operate on a real-time process model.
By ready to go, it means that any user can link its original data source with a hot site for a successful backup of their data.
The main feature of a hot site is; it runs on a parallel basis with users existing data centers, which reduces downtime issues and allows a business to run efficiently in any disaster situation.
A hot site is a ready recovery plan for any organization. It has a record of every data and all the amenities needed for a quick resumption of daily business operations in case of any disaster attack.
A cold site can be defined as more of a vacant operational space wherein facilities like electricity, communication equipment, etc. are provided.
A cold site doesn’t have any server or data backup support for the business organizations; instead, it is dependent on IT personals for setting up the necessary working equipment.
Since no initial setup is present at such a site, a client has to provide all such amenities for the proper working of a business.
Cold sites are usually used for routine backup procedures.
Cold sites are economic data storage centers as they are only used after an event of a disaster.
The cold site doesn’t have any records of backed-up data as well as information from source locations.
Also Read: 11 Best Tools for Data Governance
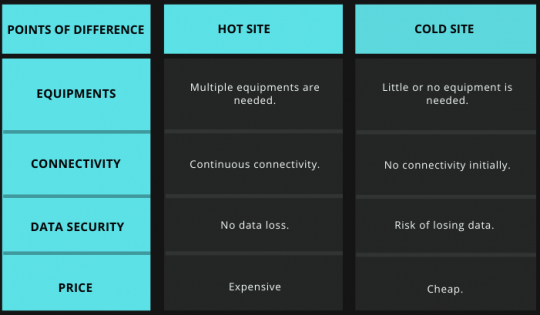
The key difference between hot site vs cold site is only in the availability or response time.
A hot site would be quickly available after any disaster attack, whereas a cold site would have to be first equipped with the necessary technical equipment for continuing operations.
Downtimes are relatively minimal within a hot site, whereas a cold site is a time-consuming process.
A hot site will need specific equipment to safeguard users' data, whereas, within a cold site, little or no equipment is needed.
Conclusion
Both hot and cold sites can play an essential role in any disaster strike. However, before choosing a data recovery site, one should discuss points like time consumption, budgets, and ease of operation.
Also Read: