The first layer of defense against unwanted access is password, but as hacking tools have advanced, password cracking has become a major danger to the security of organizations. Hackers use advanced techniques, such as brute force assaults and AI-powered breaches, to take advantage of weak passwords. By being aware of these risks and using best practices, such password managers and multi-factor authentication, sensitive data may be protected.
Let's explore the threats to your company's password security and potential remedies.
What is Password Cracking?
A method for gaining access to personal data that is applicable to organizational security is known as password cracking. As technology continues to progress, data management and protection are critical and play a key role in preventing cybercrime and hacking.
Trying a lot of different password combinations in an effort to figure out the one that works is known as password cracking. Dictionary assaults, rainbow attacks, and guessing attacks are among them. Among the methods hackers employ to obtain private information, financial data, or an individual's account.
The act of decrypting passwords to gain unauthorized access to information that should be kept private on a computer system, online account, or personal account is known as password cracking.
Data security may be enforced by creating and managing strong, one-of-a-kind passwords and updating them as needed. Nevertheless, hackers or cybercriminals can use the password cracking technique to steal and get access to sensitive and confidential data for both individuals and corporations.
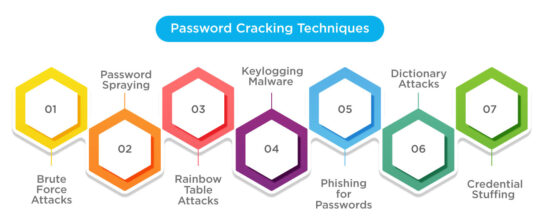
Commonly Used Password Cracking Techniques
From basic guesswork to more complex malware operations, cybercriminals use a wide range of password cracking strategies. These methods have been quite effective for hackers when combined, which is why they are still often employed. Discover the most popular password attack types here.
#1 Brute Force Attacks
Brute force attacks are one of the simplest yet most time-consuming techniques; they begin with a methodical attempt at each password combination until the right one is discovered. Weak passwords greatly increase the likelihood that these attacks will succeed. This kind of password assault may be avoided by putting strong password regulations into place and using strategies like account lockout and multi-factor authentication (MFA). It is important for businesses to balance security with convenience to be safe.
#2 Password Spraying
Password spraying is different from brute force attacks in that it entails trying a limited number of popular passwords on several accounts. Strong authentication measures that prevent password spraying include MFA and account lockouts. To improve overall defense, users should be educated about password security and the dangers of password spraying.
#3 Rainbow Table Attacks
In rainbow table attacks, related plaintext passwords are rapidly found by using precomputed tables of hash values. Using cryptographic methods like salting, which adds a random value to the password before hashing, helps prevent rainbow table attacks. Through the requirement of various kinds of verification, multi-factor authentication offers an additional degree of security.
#4 Keylogging Malware
Keyloggers silently collect keystrokes in order to get passwords and other private data. Keyloggers may be identified and eliminated by using robust endpoint security solutions, such as antivirus software. Keylogging attacks may also be avoided by following safe surfing guidelines, such as staying away from unreliable websites and updating software.
#5 Phishing for Passwords
Phishing is still one of a hacker's most effective tools. To trick consumers into disclosing their login credentials, cybercriminals use enticing emails and websites. Being alert and educated are essential for spotting and avoiding such efforts. Frequent training of staff members can reduce the likelihood of becoming a victim by enabling them to identify phishing techniques and react accordingly.
#6 Dictionary Attacks
Dictionary attacks use pre-made lists of popular words, phrases, and passwords. Because human behavior is predictable, hackers take advantage of people who employ passwords that are simple to figure out. Strong protection against dictionary attacks depends on using complicated passwords with unpredictable, one-of-a-kind possibilities. Because they can create and safely store complex passwords, password managers prove to be useful friends.
#7 Credential Stuffing
Using username and password combinations that have already been leaked or stolen to access additional accounts without authorization is known as credential stuffing. Using CAPTCHA and rate limitation, as well as requiring distinct passwords for every account, are examples of mitigation techniques. By taking these steps, automated assaults are thwarted, and hackers are deterred from using credentials they have stolen.
Best Practices to Strengthen Organizational Password Security
Implementing a complete strategy to password security may greatly decrease the risks, and strengthening organizational password security is essential to preventing data breaches and unauthorized access via password cracking. Examine the following components if you want to improve password creation and administration.
Implement Password Complexity Requirements
Strong password complexity requirements make it more difficult for hackers to figure out or decode passwords. Employers should require that employees create passwords that contain a combination of capital and lowercase letters, digits, and special characters. A strong initial line of defense against password cracking is also created by imposing minimum length restrictions and banning frequently used passwords.
Put Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) Into Practice
In addition to passwords, multi-factor authentication provides an extra degree of protection. Users must submit many kinds of identification before they may be granted access. Their biometric data, their smartphone or hardware token, or their knowledge (password) might all be examples of this. MFA can stop illegal access even if a password is compromised.
Patch and Update Software on a Regular Basis
It is essential to keep software, including operating systems, apps, and security tools, up to date. Updates for software frequently contain security fixes that fix known flaws. Updating software is a common way for hackers to obtain unauthorized access, thus patch management is crucial.
Make Use of Password Managers
Tools that safely create, store, and handle complicated passwords for a variety of accounts are called password managers. By removing the need for users to memorize several passwords, they lessen the possibility of using weak passwords. Additionally, password managers give an extra degree of protection by encrypting saved passwords.
Constant Evaluation and Enhancement of Security
Evaluate the password security procedures in place at your company on a regular basis. Conduct security audits, penetration tests, and vulnerability assessments to find flaws and potential solutions. As the threat landscape and new technologies change, modify your tactics accordingly.
The Dark Side of AI in Password Cracking and Ways to Protect Your Organization
Although artificial intelligence (AI) has transformed several sectors, password cracking is one of its negative aspects. In order to break passwords more quickly and effectively than ever before, hackers increasingly employ AI-powered tools.
Massive databases of credentials that have been stolen can be analyzed by AI, which can also spot common trends and predict passwords quite accurately. Even strong passwords are susceptible to guessing millions of password combinations in a matter of seconds using tools like dictionary attacks and brute force assaults driven by artificial intelligence.
It is essential to keep ahead of the game in order to safeguard your company. Using multi-factor authentication (MFA) will increase security. For each account, establish and save a complicated, one-of-a-kind password using a password manager. Provide staff members with regular training on password hygiene and the value of staying away from cliches.
Make an investment in cybersecurity solutions powered by AI to track and identify questionable activity instantly. By remaining vigilant, you can protect your company from the increasing risk of cyberattacks that are exacerbated by artificial intelligence.
Staying Ahead in the Battle Against Password Cracking!
The danger of password cracking is still increasing, particularly in light of the introduction of AI-powered hacking tools. Organizations can maintain security, though, by using multi-factor authentication, strong passwords, and frequent software upgrades.
Purchasing AI-powered security technologies and training staff on cyber hygiene might strengthen defenses even further. Businesses may reduce the likelihood that a password will be cracked and safeguard critical information from online attacks by being proactive and alert.
For more wisdom regarding security and technology in this digital era, keep visiting us at WisdomPlexus.
Recommended For You:
The End of the Passwords Era – Exploring Reasons and Modern Alternatives