What is Robotic Process Automation?
A business process automation technology which is based on the notion of Artificial Intelligence (AI) or software robots is called Robotic Process Automation.
An application of technology monitored by business logic and structured input for automation of business processes is known as an RPA. With the aid of RPA, an organization can configure a robot to communicate with other smart systems, to manipulate data, and to trigger responses.
The RPA tools can be used right from a simple response generation to an email to the deployment of hundreds of bots to automate jobs in a system.
The Journey of Robotic Process Automation:
Although the term ‘RPA’ was first coined in the early 2000s, it had been the work in progress even before then.
The evolution RPA took place with the help of 3 key technologies namely Artificial Intelligence, Workflow Automation, and the Screen Scraping.
It is the combination of these three systems and their evolution into one single robust tool.
What separates an RPA from the traditional workflow systems?
In conservative workflow automation tools, the developer produces a set of lists for automation of a task and with the aid of dedicated scripting language or Application Programming Interface (APIs). But, in the case of Robotic Programming Automation (RPA) Systems, the action list is developed by the observing the user performing any given task, in the Graphical User Interface (GUI) of the application and then automation is implemented by the repetition of the said tasks directly in application's GUI.
These tools come with Robust technical Specifications just like the GUI testing tools. Often, by repeating the tasks performed by the user in GUI, these tools automate interactions. The RPA tools are different from the systems which have the features which allow the data to be handled in between multiple applications. Instead, these tools use data manipulation aspect which is not what you will get in your common testing tools.
As this software tend to be more adaptive, more aware, and more susceptible to the changing environment this software proves to be more efficient and effective than your traditional workflow systems.
Once the RPA tool understands the flow of the actions and the purpose that they serve; RPA tool can then trigger responses, manipulate data, initiate new activities, and communicate with other systems seamlessly too.
The Notable Difference:
The most notable difference between the RPA and other workflow systems is that in the case of traditional systems if any particular value in the entire data is missing, the system flags up for the exception and the user has to intervene and correct the error by himself and then the system accepts the values and sends it forward for the next process.
But, in the case of RPA, as the tool is adapting, smart, and self-learning, the missing values in the data (exception) will be handled by the RPA tool itself; and smooth and seamless transfer of data will take place without involving any human interference.
Benefits of Robotic Process Automation:
- Better customer service
- Rapid completion of processes
- Ensuring Compliance with regulations and standards
- Improved efficiency with digitized and audited data
- Elimination of time-consuming and repetitive tasks
- Improvement in the employee productivity
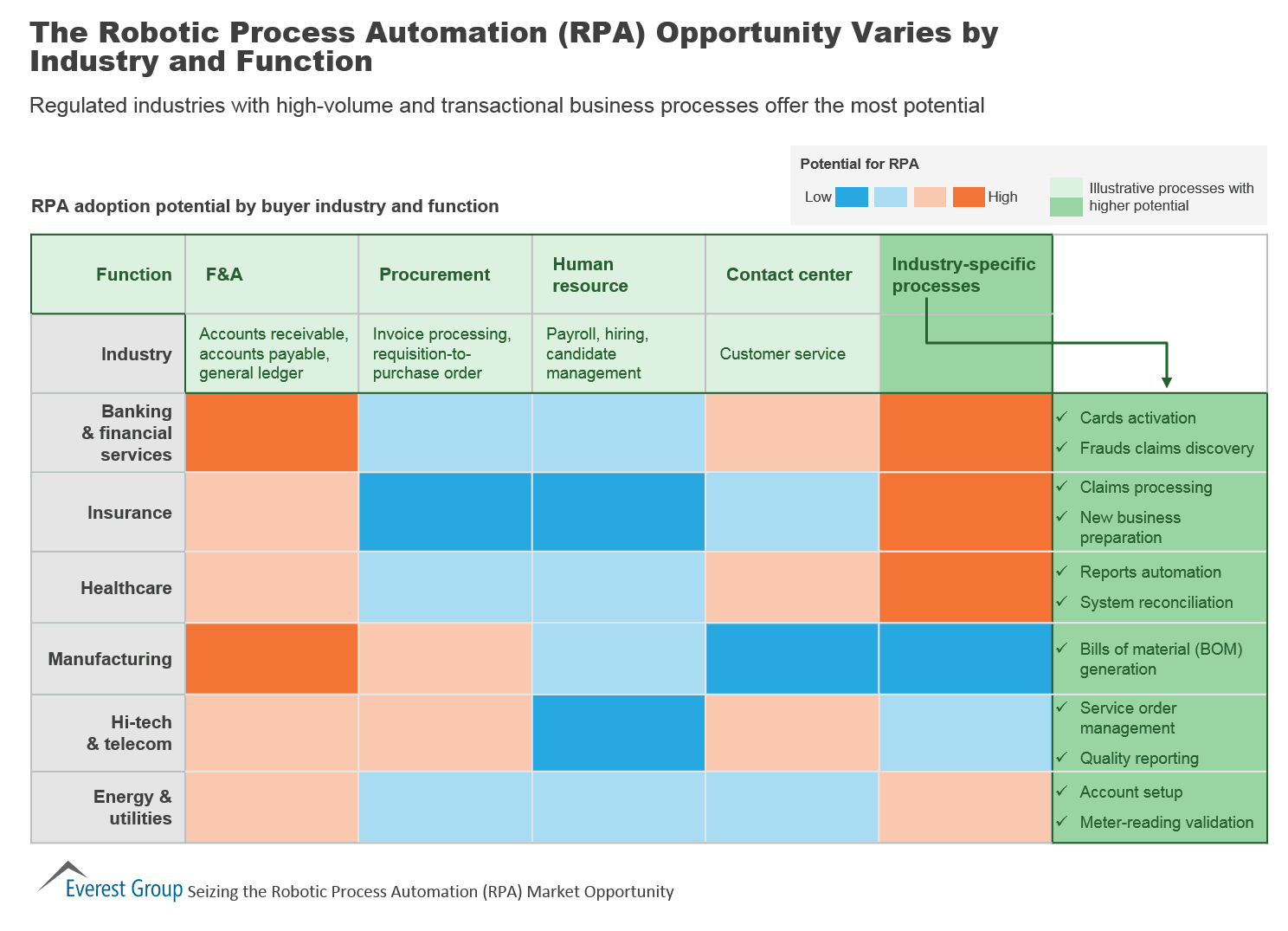
Applications of Robotic Process Automation:
Source: Everest Group
- Accounting: RPA can be used for general accounting, operational accounting, transactional budgeting and reporting.
- Customer Services: companies can offer better service to its customers by automating various tasks, inclusion of the e-signatures, verification of information, and provision of uploading documents for automated approvals or rejections.
- Financial Services: RPA tools can be used for automated opening and closing of accounts, processing insurance claims, managing audit requests, and foreign exchange payments.
- Healthcare: RPA can be implemented at medical organizations to handle patient records, customer support, billing, account management, claims, and reporting and analytics.
- Human Resource Management: HR tasks like employee information updates, timesheet submission processes, and onboarding and offboarding tasks.
- Supply Chain Management: It can be implemented for procurement, monitoring inventory levels, tracking the shipment, and by automating the order processing and payments.
Limitations of Robotic Process Automation:
- Installations for thousands of bots are more complex and costly than anticipated.
- The monetary outcomes of RPA implementations are far from assured at this point in time.
- The development of an optimally functional RPA is still in the early stages.
- It is not made for all enterprises due to higher installation costs.
If your organization has decided to implement Robotic Process Automation, we would recommend you to check for the following specifications for your RPA System:
Things to look for in an ideal RPA:
- Scalability: You should check whether the system is scalable to the level where it can be implemented for an entire organization.
- Speed: It should be able to design robotic processes in a few hours or less; the optimization should be quicker.
- Reliability: Organizations should look for the tools with built-in monitoring and analytics as it would be automated for hundreds of systems.
- Simplicity: It should be simple enough to understand and employees should be able to handle various kind of works.
- Intelligence: should be able to support simple activities, read, write and analyze the data source, and should be able to learn from the previous decisions to make smart decisions.
- Made for Enterprises: organizations should look for the RPA tools which are scalable, reliable and manageable for an Enterprise class solution.
Recommended For You: