Did you know that unpatched software is one of the top reasons for cyberattacks worldwide? Patch management serves as a barrier that safeguards your systems, information, and reputation in addition to being a standard IT responsibility.
This blog explains the lifecycle, importance, and advantages of patch management to assist your business stay secure and competitive. Let’s start!
Exploring the Concept of Patch Management
It is the process of updating firmware, drivers, and software to guard against security flaws. In addition to ensuring optimal system performance, effective patch management increases productivity.
All systems must be protected, whether they are staff laptops or PC-based devices that are not user-controlled, such as digital signs or kiosks. Ignoring patch management may put your company at risk for breaches and leaks, as well as for decreased productivity and reputational damage.
Why Do Firms Need Patch Management?
It is an essential procedure for preserving sensitive data, lowering the risk of cyberattacks, securing an organization's IT infrastructure, and guaranteeing regulatory compliance. Enhanced security, system stability and uptime, cost savings, regulatory compliance, and better performance and features are just a few advantages it provides.
By minimizing the attack surface, routine patching stops hackers from taking advantage of unpatched vulnerabilities. It guarantees more seamless operations by reducing unplanned downtime that can interfere with essential services. Additionally, patch management promotes confidence among stakeholders and customers while preventing regulatory fines.
Patches provide feature upgrades and performance improvements, guaranteeing effective systems and using the most recent advancements. All things considered, a safe and secure IT infrastructure depends on efficient patch administration.
Lifecycle of Patch Management
It is a continuous process having many steps. These much of steps take care of the ultimate patch management process. They guarantee that patches are found, ranked, tested, and implemented effectively throughout a firm. The following is a simple explanation of the patch management lifecycle:
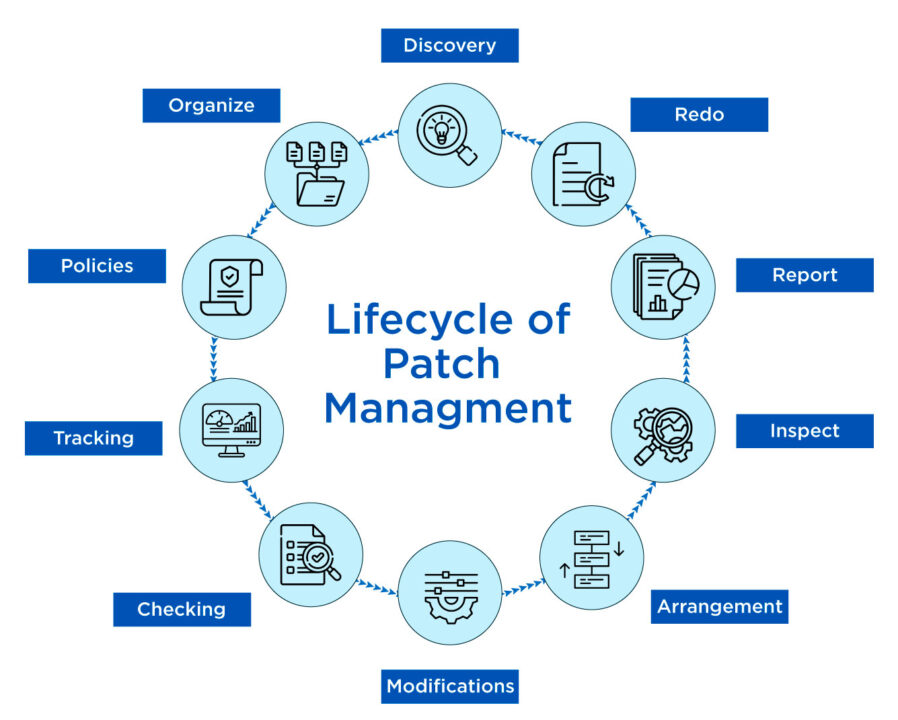
Stage 1 - Discovery:
A network inventory, which lists all of the IT resources on a network, is necessary before a patch management procedure is put into place. A team must use network assessment software to do a complete network examination in order to create an exhaustive network inventory.
Stage 2 - Organize:
A team can rank the vulnerabilities and dangers found during the inspection after completing a network evaluation and realizing the present IT environment. In the subsequent phases, build more focused patching policies by classifying people and/or systems according to risk and priority.
Stage 3 - Policies:
After successfully classifying individuals and/or systems, an organization may now develop patch management guidelines. Setting up and managing patching requirements is made easy for users by the plain and easy procedure of creating an efficient and scalable patching strategy. What must be patched, when it must be patched, and under what circumstances are determined by these patching requirements, also known as criteria.
Stage 4 - Tracking:
A team will be tracking vendors for vulnerabilities and new patches throughout this phase. Instead of maintaining track manually, businesses often set up a system to get information from vendors about impending patches and vulnerability updates.
Stage 5 - Checking:
To spot unknown issues prior to the patches being released, an IT team typically employs a test environment for testing patches. Before proceeding to the next phase of the patching lifecycle, an organization should make sure that the patches function as intended and that they roll out to the test environment successfully.
Stage 6 - Modifications:
To keep the whole IT staff and other people of a company in sync, documentation is essential, even if it can be challenging. Prior to patch deployment, take note of any modifications that will be performed.
Stage 7 - Arrangement:
It's now time to apply patches in line with the stage three patch management guidelines. At this point, it will be decided whether patches work or whether adjustments are required.
Stage 8 - Inspect:
Patch failures or pending issues can occasionally occur after deployment. If there are any incompatibilities or performance concerns, keep a careful eye on these issues and notify end users of them as well as any impending patches.
Stage 9 - Report:
Using a patch compliance report, executives and other departments may learn more about your present IT infrastructure and the impact of patching. A monthly patch compliance report should ideally be produced.
Stage 10 - Redo:
The last stage of the patch management lifecycle consists of reviewing, updating, and repeating stages one through nine. An IT team will be able to improve and streamline all patch management procedures by keeping information current and correct.
What are the Benefits of Patch Management?
Extra safe surroundings:
Patching issues on a regular basis helps to control and lower the risk in the surroundings. This minimizes the chance of security breaches at your company.
Contented customers:
You understand how important it is that the technology functions properly if your company offers a product or service that requires users to use it. The practice of resolving software issues through patch management keeps your systems operational.
Avoid needless penalties:
Regulatory agencies may impose financial penalties on your company if it fails to patch and, as a result, fails to fulfill compliance requirements. Compliance is guaranteed by effective patch management.
Ongoing product innovation:
You may upgrade your technology with patches that provide new features and capabilities. This can give your company a means to extensively implement your most recent software advancements.
Wrapping Up Thoughts!
Impactful patch management is the backbone of a safe IT environment. From mitigating risks to driving innovation, patching ensures optimal performance and safety. By implementing the above-mentioned 10 stages of the lifecycle, organizations can safeguard their systems, avoid penalties, and build trust with stakeholders, ensuring a future-ready digital ecosystem.
For more informative and engaging content, visit us at WisdomPlexus.
Frequently Asked Questions:
Q1: What are the three types of patch management?
Ans: Bug fixes, feature upgrades, and security patches are the three most popular types of patches.
Q2: What is the purpose of a patch?
Ans: An operating system or piece of software can be updated with a patch to minimize vulnerabilities, enhance functionality, or correct defects. Patches are created and tested, and either a person or an automated tool can apply them. \
Q3: What is the scope of patch management?
Ans: In patch management, hardware and software are updated, patches are tested and verified, the procedure is documented, regulatory compliance is ensured, data is protected from cyber threats, and system performance is enhanced for productivity.
Recommended For You:
List of 11 Patch Management Best Practices: You Should Follow




