Cyberattacks aren’t just about fancy hacking tools; they’re often about tricking people. Social engineering is all about manipulating human emotions, like trust or fear, to get sensitive information or access.
It’s sneaky because it doesn’t attack your computer; it targets you. In this blog, we’ll uncover how social engineering works, explore common scams, and share easy ways to stay safe in a world of digital fraud. Let’s start!
What is Social Engineering? When Cyber Threats Target the Human Mind
A wide range of harmful behaviors carried out through human interactions are collectively referred to as social engineering. It cheats users into making security errors or disclosing private information by manipulating their minds.
Attacks using social engineering can take one or more steps. To get the background information required to carry out the assault, including possible points of entry and lax security measures, a criminal first investigates the target. The attacker next makes an effort to win the victim's confidence and set the stage for further acts that violate security procedures, including disclosing private data or allowing access to vital resources.
How Does It Work? The Mechanics of Social Engineering
Instead of employing violent techniques, social engineering attacks encourage users to compromise themselves by fostering conversation between the attacker and the victim. The attack cycle entails obtaining background data, penetrating through relationships based on trust, taking advantage of the victim once vulnerabilities and trust have been created, and disengaging once the intended action has been completed.
Emails, social media discussions, and in-person meetings are just a few of the ways that this process might occur. Because social engineering may provide hackers access to several networks and accounts, it is essential to be mindful of it. They can also increase malware and sneak money. The use of social engineering as a deceptive tactic must be avoided.
Types of Social Engineering Attacks
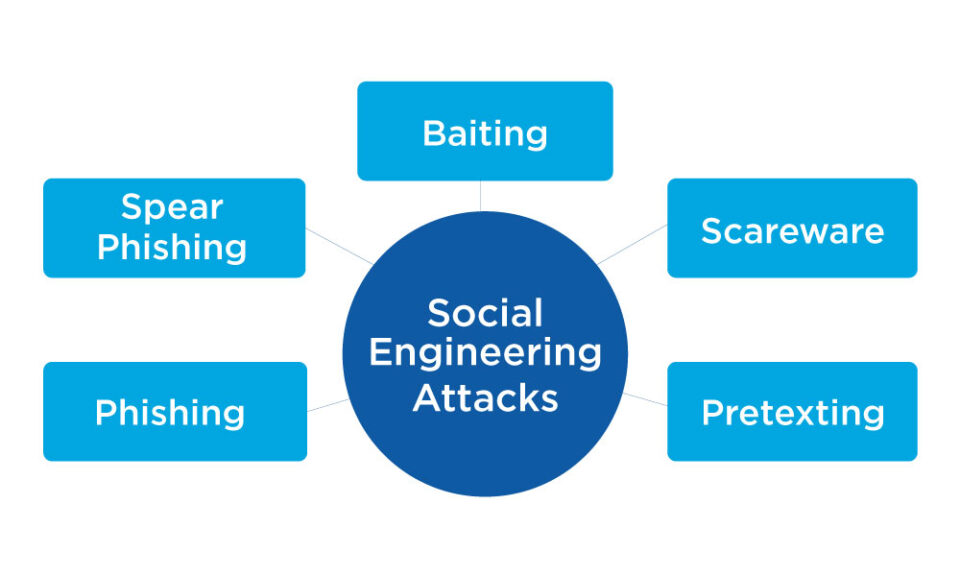
Social engineering assaults use human behavior manipulation to get private information or do harmful tasks.
- Baiting
Baiting takes advantage of a victim's greed by making false promises. In the hopes that victims would plug them into their PCs, attackers may physically place malware-infected USB devices in conspicuous places, such as parking lots or elevators. Digitally, baiting frequently takes the form of attractive advertisements or software downloads that infect computers with malicious software.
- Scareware
Scareware convinces victims that their gadgets are in danger by bombarding them with fictitious threats or alerts. Pop-ups, for instance, can assert that the machine is compromised and provide a malevolent fix. Victims could unintentionally access fraudulent websites or download dangerous malware. Spam emails that promote malware or provide phony services are another way that scareware spreads.
- Pretexting
This technique entails fabricating complex falsehoods in order to obtain private information. Attackers frequently urge victims to confirm their identity while posing as reliable individuals, such as bank employees, law enforcement, or coworkers. They get personal information from these exchanges, such as access credentials, bank details, and social security numbers.
- Phishing
Mass emails or texts are used in phishing schemes to generate anxiety, curiosity, or a sense of urgency. The victims are deceived into downloading malware, clicking on harmful links, or divulging private information. To seem convincing, attackers frequently imitate reputable institutions, such as banks.
- Spear Phishing
Spear phishing targets particular people or organizations, in contrast to regular phishing. To create compelling, customized communications, attackers compile comprehensive information about their victims. For example, they can pose as a reliable IT specialist and ask victims to reset their passwords by clicking on a fraudulent link. Because of this customized strategy, it is more impactful and tough to identify.
Social Engineering Prevention Techniques - Proven Ways to Defend
- Pause Before Responding
Take a minute if you are contacted by phone, text, or email requesting urgent action or sensitive information. Hurry and panic are key components of cybercrime. Does this seem strange to you? Before acting, confirm the request.
- Preview links
Drag your cursor over any link in an email or message to view the URL before clicking on it. Don't click if the address seems odd or doesn't match the sender's official website.
- Set Up Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
2FA adds an additional step that is impossible to go around, even if your password is stolen. Use built-in features on services like Gmail or authenticator applications like Google Authenticator.
- Lock Down Social Media
Sharing too much on social media might provide hackers with important details about you, such as your birthdate, location of employment, and preferred pastimes. Limit the visibility of strangers by reviewing your privacy settings.
- Challenge Unusual Requests
Call or speak with your "boss" personally if they ask for sensitive papers or gift cards over email. To take advantage of trust, social engineers frequently pose as authoritative persons.
- Be Cautious with USB Drives and Freebies
Do not install free software or use USB devices that have been found without first verifying their truthfulness. Consult an IT specialist or a reliable friend who is tech-savvy if you're not sure.
- Install Security Tools
To stop harmful pop-ups, use a browser plugin and trustworthy antivirus software. These kinds of tools serve as an additional line of protection and are reasonably priced.
Final Thoughts - Protecting Yourself in an Age of Digital Fraud
Social engineering works because it preys on trust and urgency, catching people off guard. But the good news is that a little care goes a long way. Pause before acting on strange requests, double-check links, and protect your accounts with strong security measures.
Staying aware and informed can help you outsmart these tricks and keep your information safe in today’s fast-moving digital world. Trust your instincts—they're often right!
For more insightful as well as helpful tech-savvy content, keep visiting us at WisdomPlexus.
Recommended For You:
Popular Cybersecurity Myths to Ignore in 2024
Protect Your Business from Cyber Threats: Pro Tips to Prevent Cyber Attacks