Phishing attacks are a serious danger to organizations all around the world because they take advantage of flaws in phone, SMS, and email interactions. The danger has increased due to the COVID-19, as 3.4 billion spam emails are sent every day. Malware infection, data breaches, and account compromise are all possible outcomes of these attacks.
Let’s learn about phishing attacks in this blog, including what they are, the different types, and how to prevent them.
What is a Phishing Attack?
Phishing attacks occur when someone sends a fake message that seems like it came from a reliable source. Email is typically used for this. Installing malware on the victim's computer or stealing private information, like login credentials and credit card numbers, are the objectives. To defend themselves, everyone should become aware of phishing, a prevalent form of cyberattack.
Types of Phishing Attack
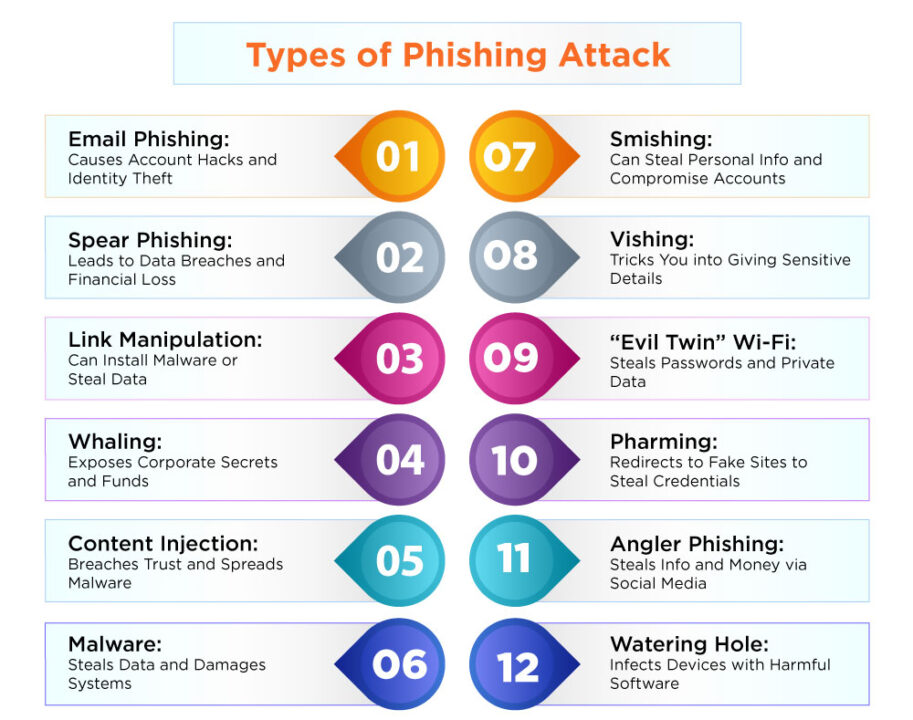
#1 Email Phishing: Causes Account Hacks and Identity Theft
It is the broad word for any fraudulent email message that aims to fool recipients into disclosing personal information. Account passwords, personally identifiable information (PII), and company trade secrets are typically the targets of attacks. Attackers who target a particular company, however, may have different goals.
#2 Spear Phishing: Leads to Data Breaches and Financial Loss
These emails are sent to targeted individuals in an organization, typically those with high-privilege accounts, in an attempt to fool them into giving money to the attacker, downloading malware, or disclosing private information.
#3 Link Manipulation: Can Install Malware or Steal Data
An illegal website that mimics the official company's website is linked in the messages, leading recipients to a server under the control of the attacker. There, users are tricked into authenticating into a phony login page that transmits credentials to the attacker.
#4 Whaling: Exposes Corporate Secrets and Funds
These communications are usually addressed to prominent workers of a firm to make them think that the CEO or another executive has asked for a money transfer. Under the general heading of phishing, CEO fraud involves an attacker impersonating the CEO of the targeted company rather than a well-known website.
#5 Content Injection: Breaches Trust and Spreads Malware
Users will be tricked into visiting an official website by an attacker who can include harmful material, which will either display them a dangerous popup or send them to a phishing website.
#6 Malware: Steals Data and Damages Systems
Malware may be downloaded onto users' devices if they are misled into opening an attachment or visiting a link.
#7 Smishing: Can Steal Personal Info and Compromise Accounts
Attackers use SMS messages to fool consumers into visiting malicious websites on their devices. A malicious link that offers discounts, awards, or free prizes is sent by attackers to a specific victim by text message.
#8 Vishing: Tricks You into Giving Sensitive Details
Voice-changing software is used by attackers to leave a voicemail instructing their intended victims to contact a number where they can be defrauded. Voice changers are also used to mask an attacker's gender or accent when conversing with targeted victims, allowing them to pose as someone they are not.
#9 “Evil Twin” Wi-Fi: Steals Passwords and Private Data
In order to carry out man-in-the-middle vulnerabilities, attackers pose as free Wi-Fi and fool users into connecting to a malicious hotspot.
#10 Pharming: Redirects to Fake Sites to Steal Credentials
Account credentials can be stolen using a two-phase assault called pharming. In the first stage, a targeted victim is infected with malware and sent to a mock website and browser, where they are duped into providing login credentials. Redirecting people to fake domains is another purpose for DNS poisoning.
#11 Angler Phishing: Steals Info and Money via Social Media
By posing as legitimate organizations on social media, attackers respond to postings and deceive users into sharing personal information and account credentials.
#12 Watering Hole: Infects Devices with Harmful Software
An attacker finds a website that many targeted people visit, takes advantage of a weakness on the website, and utilizes it to deceive users into downloading malware since a hacked site offers countless possibilities. When malware is placed on the computers of the targeted users, the attacker can either send a payload to the local network to steal data or reroute users to fake websites.
What can Organizations do to Prevent Phishing?
-
- Obtain free anti-phishing accessories
- Create secure passwords and turn on two-factor authentication.
- Pay attention to update messages.
- When opening emails or clicking links, be cautious.
- Don't provide your details to an unprotected website.
- Use anti-phishing software.
Being Alert is the Key to Safety!
Awareness and attentiveness may greatly lower the danger of phishing assaults, which are a serious concern. People and businesses may safeguard themselves by practicing multi-factor authentication, avoiding dubious websites and emails, and keeping up with the many forms of phishing.
To keep ahead of these evolving cyber threats, it's also essential to use anti-phishing technologies and update software on a regular basis. Always be on the lookout for measures to protect your organizational and personal information against phishing schemes.
As you reach the end, it implies you are interested in this topic, so for more similar insightful content, keep visiting us at WisdomPlexus.
FAQs
1. Which phishing attack is most common?
The most common phishing attack is email phishing.
2. What is online phishing?
An online scam known as "online phishing" deceives people into divulging personal information by using phony emails, SMS, or webpages. By gaining sensitive information such as passwords, bank account information, or credit card numbers, the intention is to steal money or identity.
3. Why are phishing attacks so successful?
Phishing attacks are effective because they take advantage of human psychology and are rather easy to carry out.
Recommended For You:




