Supervised learning and unsupervised learning are the two popular and commonly used machine learning approaches. Companies are adopting ML technology to make things easier and smarter; the technology is going above and beyond in different sectors such as facial recognition, healthcare, finance, and more.
Now, there are two common approaches to machine learning (ML): supervised learning and unsupervised learning. Supervised learning uses labeled data to predict outcomes, whereas unsupervised learning does not work. Instead, use raw or unlabeled data, for example: grouping customers based on their purchase behavior. Alongside, both differ in certain aspects you need to understand.
This blog breaks down the key differences between supervised learning and unsupervised learning, so you know how to pick the right learning option for your needs.
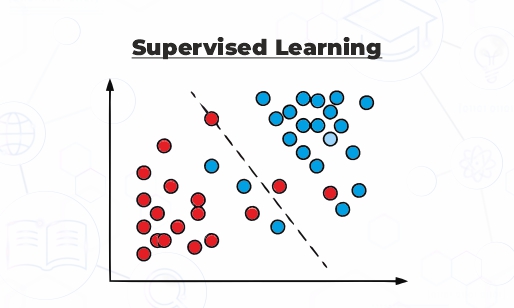
What is Supervised Learning?
Supervised learning is a popular machine learning technique wherein ML systems are trained using labeled data. Here, “labeled” means every training data set has a paired output. By learning the relationship between the data and its label, the model can predict new, unseen data.
Let’s take a simple example of school, wherein a teacher gives examples (labeled data) and explains the concepts with correct answers (output)
-
- Shows students pictures of animals and labels them as a cat and a lion.
- The child learns the difference between a cat and a lion.
- If the student makes a mistake, the teacher corrects it with the right answer
- This is how supervised learning works. It learns from the trained machine data and makes predictions.
Types of Supervised Learning
Classification: Useful in predicting categories or classes.
Regression: Can predict the numerical values.
Pros of Supervised Learning
-
- Higher accuracy with labeled data
- Performance can be easily measured with known outputs
- Can handle a range of tasks using regression and classification
Common Use Cases
-
- Detect spam emails – spam/not spam
- Credit scoring
- Image recognition
- Medical diagnosis and predictions
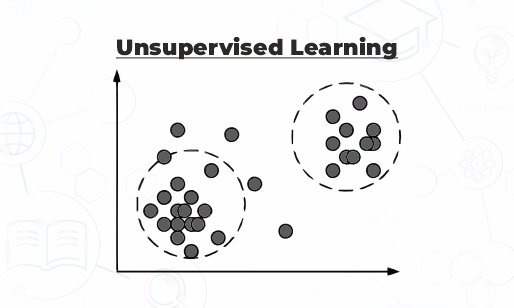
What is Unsupervised Learning?
In unsupervised learning, the target output is not known, and the data is unlabeled. It uses machine learning algorithms to find hidden patterns in data without human intervention. It works independently, discovers data on its own, identifies patterns, relationships, and more.
To explain unsupervised learning, let’s take an example: financial institutions adopt unsupervised learning to keep a check on financial transactions. It is used to detect suspicious financial activities that are different from normal behavior. This can help detect fraud and theft in real time. You can also segment customers by behavior.
Types of Unsupervised Learning
-
- Clustering
- Association
- Dimensionality Reduction
Pros of Unsupervised Learning
-
- Works on raw or unlabeled data
- Can handle large volumes of data
- Uncover hidden insights and trends
Use Cases
-
- Fraud detection
- Customer segmentation
Even though the type of data is the easiest way to differentiate between the two machine learning models, they differ in terms of their goals and applications.
Supervised Learning vs Unsupervised Learning: Key Differences
Parameter |
Supervised Learning |
Unsupervised Learning |
| Input Data | Here, the data is in a labeled format. Meaning, learns from a labeled data where input and output are known | Here, the data is unlabeled, which means only input data is available, and no output or labeled data. |
| Computational complexity | Simple | Complex |
| Primary Goal | The main goal is to predict outcomes or classify data | The goal is to discover hidden patterns or structures in data |
| Common Models | This includes Classification, Regression
Classification: Decision Trees, Support Vector Machines, Naive Bayes, K-nearest Neighbor Regression: Linear Regression, Decision Tree Regression, Polynomial Regression |
This includes Association, Clustering, Dimensionality Reduction
Clustering: K-means Clustering, Gaussian Mixture Models, DBSCAN Dimensionality Reduction: t-SNE |
| Accuracy | The accuracy level is higher in supervised learning | The accuracy level is less in unsupervised learning |
| Examples | Ideally used for spam detection, image classification, and more. | Ideally used for anamoly detection, customer segmentation |
Supervised vs Unsupervised Learning: Which One to Opt?
The context is simple; you can use supervised learning to solve problems with labeled data and known outputs. As mentioned above, it is used in scenarios such as image recognition, spam email detection, and more.
Alternatively, in unsupervised learning, the data is unlabeled and used to discover patterns or detect defects. Everyday use cases include market basket analysis, anomaly detection, and customer segmentation. The
Wrapping it Up
Both supervised learning and unsupervised learning are crucial techniques in machine learning. Understanding the key differences between the two is essential to making a well-informed decision for your business goals.
Supervised learning is ideal for precision-oriented, highly labeled settings, and self-supervised learning opens the door to large unlabeled datasets and shapes the future of AI models. Organizations can make the right decision by choosing the right approach and preparing future-ready AI solutions.
Our site is packed with insightful and feature-rich content. Visit us now to stay tuned to more such blogs.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q. Which are the four types of ML?
Ans: The four common types of ML are: Supervised learning, Unsupervised learning, Semi-supervised learning, and Reinforcement learning.
Q. What is the main difference between supervised learning and unsupervised learning?
Ans: Supervised learning is based on labeled data, and unsupervised learning is based on unlabeled data.
Recommended For You:
AI-Powered Underwriting: Transforming the MGA’s Underwriting Process with Machine Learning
A Rundown of Top 5 Machine-Learning Trends Shaping 2025 and Beyond