Complications in storing data accurately can hamper the day-to-day processes and growth of the company as well.
Therefore, handling this ever-growing data created a massive need for a framework that could manage this.
Data governance is the set of principles that ensure the efficient quality of data throughout its lifecycle.
To put it in brief, data governance ensures integrity as well as the security of data.
Let us take a look at some of the components of Data Governance.
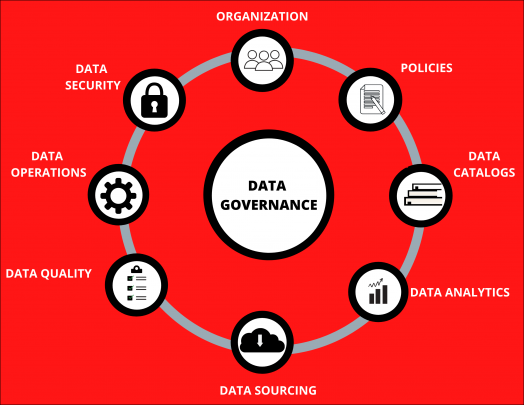
- Components of Data Governance
- Why Follow the Data Governance Lifecycle?
- Steps Involved in Data Governance
- Charting Out Strategy
- Selecting the Right Data Governance Model
- Selecting the Right Hierarchy For an Organization
- Selecting the advisory committee
- Setting up the Data Governance Office
- Selecting the Data Governance Working Group
- Data Governance Support Team
- Policy Enforcement
- Creating Skilled Business Teams
- A skilled IT team
- Flow Chart Diagram
It has to be ensured that the data that is entering the organization is clean. Contaminated data may disturb the efficiency of the processes.
Not only at the front-end, but quality at the back end, which includes legacy systems, also has to be maintained.
Security in combination with privacy is most needed.
The data that is being collected needs to be kept safe from attacks.
The privacy of the collected data also has to be maintained, keeping into consideration the privacy laws.
Its aim is to apply the practices and technologies much needed for safeguarding the integrity and accuracy of data.
MDM only improves the quality of data to a certain extent, but data governance is needed to maintain the quality in the long term.
Data stewardship is the process of managing an organization’s data assets, wherein users are provided with high-quality data for usage.
A data steward is a person who is responsible for executing data usage as well as security policies.
It provides an understanding related to existing data and its journey throughout the organization.
Data governance becomes much easier with optimized data architecture.
Abiding by the data governance lifecycle can bring a lot of data-related improvements in the organization. Some of them are discussed below:
-
- Data security is enhanced as the main focus is on establishing data ownership.
- Breaks down data silos in organizations.
- Ensures compliance with privacy laws and other statutory regulations.
- Data governance helps companies understand their growth journey by assisting them in evaluating the organized data.
- It helps in simplifying data storage and data backup.
Also Read: Hot Site vs. Cold Site: Understand the Difference
Prepare a charter for the company, defining its mission and goals.
The charter will be created with the help of the stakeholders as well as the people involved in the projects of the company.
The data governance structure is defined in the charter.
It also explains the authority related to the handling of the data.
There are many data governance models.
Not every data governance model fits every organization.
A standard data governance model will mainly include the following:
-
- Senior executives; making senior-level decisions.
- Middle management.
- Data Governance office, offering guidance.
- Data governing working group, executing all administrative work.
Two types of data governance hierarchy are usually considered.
First one, starting from corporate governance to IT governance then towards data warehouse governance and lastly data governance.
The second one is the exact opposite of the first.
Here the top-level starts from Data governance to corporate governance than to IT governance, and lastly, data warehouse governance.
In the second hierarchy, preference is given to data governance.
It makes sure that all the data is entirely following the statutory rules and regulations.
The decision to select the data governance hierarchy ultimately resides with the management, wherein they have to decide on the approach they are willing to use.
They can either opt for a corporate governance approach or a data governance approach.
The IT governance step defines the execution of the data strategies within systems.
They also hold the position as to who will be making certain decisions regarding infrastructure as well as architecture.
Lastly, data warehouse governance makes sure to select the model, ensuring its usage in compliance with any of the policies.
The advisory committee or the steering committee is responsible for implementing the data governance process across the organization.
It also prioritizes the data governance programs as well as sponsors them.
The committee has the power to make changes in the projects and recommends the projects, along with approving the finance for the same.
The advisory committee is expected to be a part of everything that is related to data governance.
This committee consists of the following:
-
- Senior vice president.
- Vice president.
- Executive sponsors in business as well as IT.
Senior vice president and vice president should be from the field as of data that is being governed.
The data governance office is responsible for enforcing data governance. Members of the same include the data governance lead, the IT representative, and the coordinators.
DGL works closely with every business unit to ensure that governance strategies are common throughout the organization.
The DGL should be the leader, having complete knowledge of key influencers.IT representative has the responsibility of tackling issues related to technology.
Data governance coordinators are trusted with work like meeting schedules, updating issue logs, etc.
This group is trusted with the responsibility of driving quality for specific subject areas related to the business.
They recommend projects on the basis of data.
The following roles are included in it:
-
- Data quality lead.
- Data steward.
- Metadata lead.
- Data architect.
The IT group is expected to be competitive regarding the knowledge of data modelling, data analysis, and migration.
The team includes the following roles:
-
- Data owner: Creates policies and is the contact person for any data-related issue.
- Data Steward: Ensuring minimum data quality issues and making sure that no duplicate data exists in other departments.
- Data Architect: The job of a data architect is to create a structure and organize quality data for business processing.
- Data Modeler: Creates rules for data quality.
- Data Analyst: Analyzes and researches the problems for the data owners.
One of the ways to improve the quality of data is to implement better data handling and management practices.
A data quality team, when kept in close guidance of executive-level sponsorship, ensures that the best practices for data quality are enforced.
Policies are created in accordance with the charter of the organization through the data governance working group.
These policies are made for the handling of data, conflict resolution, etc.
Policies are better executed when they are understandable to everyone.
The two pillars of data governance are business experts and IT experts.
Business experts are the ones who have knowledge related to business needs. They bring up the requirement like what business needs are in relation to data.
IT team makes it sure to provide the best technical know-how for the smooth processing of data governance.
Business experts are trusted with the responsibility related to overcoming the poor data into the systems and developing a plan to correct it.
The business team handles matters related to the policies and their enforcement.
The IT team, on the other hand, ensures the compliance of data and security features.
IT team members provide tools that can work best on data with the business team.
IT teams are expected to work closely with other organizational teams and understand their data requirements, and provide suitable applications to handle the data.
Conclusion: Data Governance Lifecycle
Data governance is a continuous process. The only implementation of the same is of no use. For data governance to be effective, it has to be regularly updated because data, regulations, and usage keep on changing too.
Also Read: 6 Best Practices for Data Governance