Cloud computing has some basic forms of delivery; these bases are divided into three different structures: IaaS, SaaS, and PaaS. Depending on the needs, the user can choose one of the three models.
Before choosing the infrastructure provider, cloud users must precisely identify the solution that best suits their situation.
In this article, we’ll compare & address the difference between the IaaS and SaaS models. This will help you opt for the cloud solution most suited to your operating modes.
IaaS vs. SaaS: On the Basis of their Definition, Use & More
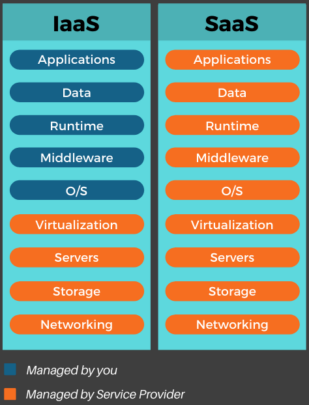
In the IaaS cloud computing model, the user manages the operating system, server middleware, and application software. Server hardware, virtualization layers, storage, and network are the responsibility of the provider.
The IaaS model allows the hardware infrastructure to be upgraded on demand and remotely. The use of an IaaS allows the development of programs and tests, the implementation of complex storage and backup solutions, and the analysis of big data.
Key advantages of IaaS:
-
- Useful for backing up, storing, and recovering data.
- It helps manage fluctuating storage needs.
- Setting up test and development environments is also faster and cheaper with IaaS.
- Easy connection of several company sites to the leased IaaS environment.
- Allows users to significantly increase their computing power.
Common examples of IaaS providers include Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure and Google Compute Engine (GCE).
The IaaS solution is extremely dynamic and flexible. It allows companies to have absolute control over their infrastructure as well as to connect multiple users to the same machine.
IaaS is a very good option for fast-growing companies because your server can evolve as your business grows.
It is important to emphasize that it is recommended to have in-depth computer knowledge to be able to take all the benefits offered by this model.
All types of infrastructure are possible in the cloud. For seasonal environments, there are resources where this scenario fits perfectly.
It is possible to have web portals that require instantaneous scheduling, replication of on-premises and hybrid environments. It can be used by companies that grow quickly or prefer OpEx.
Also Discover: 6 Best Use Cases for IaaS
In SaaS, you have access to application services installed on a server. You don't have to worry about installing, maintaining, or coding this software.
Most of the SaaS applications can be administered instantly from a web browser without requiring any installation or downloads. Although some might need plugin installation.
It is easy for organizations to streamline their management and support, as everything can be managed by suppliers.
Maintenance, installation or help for the software will be provided by the SaaS service provider and you will only have to pay for your use.
Key advantages of SaaS:
-
- The applications are updated automatically.
- Mobility of use.
- Access to on-demand features.
Common examples of SaaS providers include Google Apps, Cisco WebEx, Dropbox, and Citrix GoToMeeting.
SaaS solutions can be a very attractive option for SMEs. This way, they need not download or install different software on each computer.
SaaS also greatly facilitates businesses by delegating all support to software providers and not to an internal IT team.
When there is a need to reduce the cost of software ownership, removing the need for technical staff to manage to installation and update the software, as well as reducing software licensing costs.
Also, it is useful for collaborative remote access and software editing needs, or even for short-term software purchases.
Basically, what differentiates these two models is the freedom that the company has with the applications and how much is managed by the cloud services provider itself.
With IaaS, the customer has control over the operating system and can develop their own applications, run systems, and software that they want, and create platforms. The provider is responsible for maintaining the physical and virtualization infrastructure.
Whereas SaaS offers ready-to-use solutions that meet a specific business need. The customer only uses the software via the internet, and the provider is responsible for managing the infrastructure and platform.
You may also like to read: