Rapid Application Development is a team-based technique which is based on prototyping and iterative development where no detailed pre-planning is involved.
RAD implements the complete methodology of a four-phase life-cycle. It is used when a system needs to support a company’s new business function.
The main objective of RAD is to cut the development time and its costs by incorporating users in every phase used in RAD.
With Rapid Application Development, developers can update software quickly and adds multiple iterations without needing to start from the beginning.
It is an improvement over the previously used traditional waterfall model, which was more complex as in that case, it was very difficult to change the core functions and features when it went into the testing phase. It was less useful as it didn’t fit the evolving environment of any company.
-
- Requirement planning: In this phase, the RAD team (users, managers, and IT staff) agree upon the business needs, project scope, and system requirements.
- User Design: The purpose is to give the users an idea of the features and ensure that there are no bugs in the coding.
- Construction: The users continue to participate by suggesting improvements or changes during the development process. The main motive for the developers is to get the project’s end product to align with the user’s vision.
- Cutover: Tasks like data conversion, testing, the changeover to the new system, and user training are included. The reliability and stability of the software are checked for which the final round of testing is done.
6 Pros of Rapid Application Development
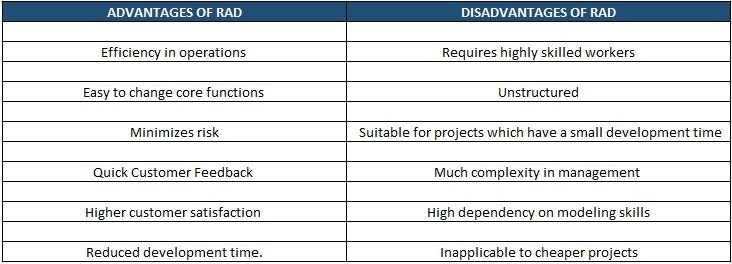
Rapid application development allows the quick testing of prototypes for various functions and features. The end product has stability, usability, and maintainability.
It is effortless in changing the core functions of the software when the program is in the testing phase. The prototypes are individually tested at every iteration, which reduces the overall testing time.
It mainly focuses on the business problems that are important to the end-user. The software is more useful as it involves an evolving prototype suitable for business functionality.
More feedback leads to higher customer satisfaction and better quality of the end product, i.e., software.
It has minimal documentation. RAD tools are automated which makes it an easy and quick way to make prototypes.
Due to various prototypes available, the risk is minimized as the RAD approach analyzes the risk factors from the early part of the process. Risk control is a critical feature that RAD offers.
RAD is a decision-maker that sets a time limit to complete a project. Generator RAD has used in the form of spreadsheets and domain-specific languages.
Composition RAD is more scalable than GRED. It builds a framework and database management systems.
-
- Requires highly skilled workers and a strong collaboration between teams to secure a commitment to the involvement of users.
- The cost of code generation is significantly high, it is not the best fit for projects with low-cost margin.
- The model has rigidity as all the requirements must be known before the project starts.
- It is much unstructured, and the stages are not well defined.
RAD in Centric Consulting
This software company used the RAD model that easily interfaced with the customers. Using the RAD model, they quickly understood the needs and requirements of their client.
The customer was able to give inputs on their condition, which sped up the process and saved time. As it’s different prototypes were open for testing by the user, it also saved costs because of the open-source infrastructure.
You May Also Like To Read:
Microservices vs. Web Services: How the two Software Development Architecture Differ?
Data Warehouse vs. Data Mart: What’s the Difference?